In Windows 10 and 11, the Local Security Policy lets you manage different security settings, such as account policies, local policies, public key policies, event logs, and so on. It is important to note that the Local Security Policy is only available in the Windows 11 Pro, Enterprise, and Education editions. With this out of the way, let’s begin with the article.
1. Open Local Security Policy Using Windows Search
Whether on Windows 10 or 11, a quick search gets your desired installed app in front of you. It is one of the simplest and most common methods for accessing the Local Security Policy. If you are new to Windows, this should be your go-to way. Here’s how. Step 1: Press the Windows key on your keyboard or click the on-screen Windows icon. Note: You may also click on the on-screen search icon.
Step 2: Type ‘Local Security Policy.’
Step 3: Click ‘Run as administrator.’
In the prompt, select Yes. That’s it. You have successfully opened the Local Security Policy without having to go through much hassle. If you cannot see the search bar on your Windows PC, fix the missing search bar.
2. Run Local Security Policy From Windows Tool/Administrative Tools
Windows Tools (Windows 11) / Administrative Tools (Windows 10) are collections of system tools and utilities built into the Windows operating system. These tools and utilities assist you in managing, troubleshooting, and diagnosing various computer issues. It includes several built-in features, including Disk Cleanup, Disk Defragmenter, and System Configuration. One of the tools included in Windows Tools is the Task Scheduler. Step 1: Press the Windows key on the keyboard or click the Windows icon on the taskbar and select All apps.
Step 2: From the list of programs, scroll down and click on Windows Tools. Note: If you are on Windows 10, find the Windows Administrative Tool.
Step 3: Finally, click on the Local Security Policy.
There you go. You have successfully opened the Local Security Policy on your Windows PC. There are multiple ways to access Windows Tools if you don’t want to access it from the Start Menu.
3. Open Local Security Policy Using File Explorer
This method enables you to open Local Security Policy from File Explorer. Whether you’re using Windows 10 or Windows 11, it’s not too hard to follow the below steps. Step 1: Press the Windows key on your keyboard, type File Explorer, and click Open. Note: Alternatively, you can press the ‘Windows key + E’ on your keyboard to open Windows Explorer.
Step 2: Navigate to the address bar, type the below command, and hit Enter.
There you go. You can get started with local security policy in a few simple steps. Additionally, you can also create a shortcut and place it anywhere you prefer on your Windows PC. Let’s understand how.
4. Create a Desktop Shortcut to Run Local Security Policy
Creating a Local Security Policy shortcut on the desktop is a one-time process. It allows you to access the tool with a click whenever you wish to. Follow the below steps. Step 1: Right-click on the empty space on your desktop, go to New, and select Shortcut.
Step 2: In the Create Shortcut wizard, type secpol.msc under ‘Type the location for the item’ and then click Next.
Step 3: Enter a name for your shortcut and click Finish. Eg: Local Security Policy
You can access the Local Security Policy by pressing a button at any time.
5. Open Local Security Policy Using Task Manager
Be it for monitoring your PC’s performance or to end any task, Task Manager is commonly used. Opening the Local Security Policy from the Task Manager is pretty simple. All you need to do is follow the instructions below. Step 1: Press the Windows key on your keyboard, type Task Manager, and click Open. Note: Alternatively, press ‘Windows key + Shift + Esc’ to open Task Manager.
Step 2: Click on ‘Run new task.’ Note: If you are on Windows 10, you will have to click on File and select ‘Run new task.’
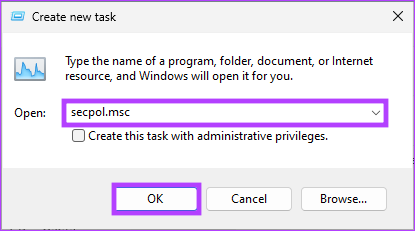
Step 3: In the ‘Create new task’ window, in the text field, type secpol.msc, and click OK.
You have now opened Local Security Policy on your Windows PC using Task Manager. You can do the same with the Run command box. Keep reading.
6. Open Windows 11 Local Security Policy Using Secpol.msc Command
Since you already know how to open Local Security Policy with Task Manager (see above), this method is easy. Follow the below steps. Step 1: Press the ‘Windows key + R’ to open the Run command box.
Step 2: Now, type the below command and click OK.
There you have it. This method is the quickest way to open the Local Security Policy.
7. Run Local Security Policy Using Command Prompt or Windows PowerShell
You can launch Local Security Policy using command-line interpreters. All you have to do is enter a command to open it. Follow the below steps. Step 1: Press the Windows key on your keyboard, type Command Prompt or PowerShell or Windows Terminal, and click ‘Run as administrator.’ Note: For the demonstration, we are going with Command Prompt.
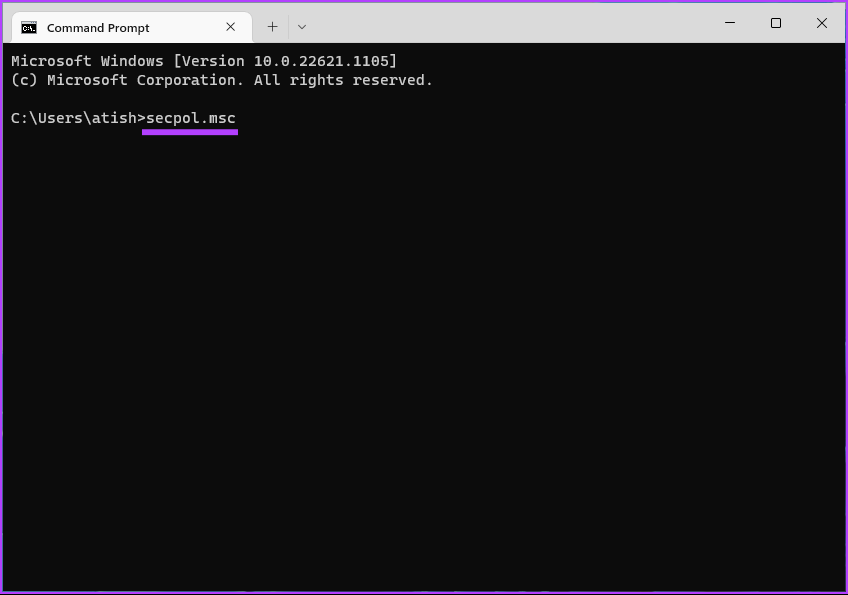
In the prompt, select Yes. Step 2: Type the below command and hit Enter.
That’s it. It will open Local Security Policy with ease. If you don’t want to use Command Prompt or PowerShell, you can try the next method.
8. Open Local Security Policy Using Group Policy
Group Policy Editor is an excellent tool for managing Windows settings, including the Windows Firewall. Here’s how you can open Local Security Policy in Windows 11 using Group Policy. Step 1: Press the Windows keys on your keyboard, type gpedit, and click Open. Note: You can also press ‘Windows key + R’ to open the Run command box, type gpedit.msc, and click Open.
Step 2: In the left pane, under ‘Local Computer Policy,’ select Computer Configuration.
Step 3: In the right pane, double-click on Windows Settings.
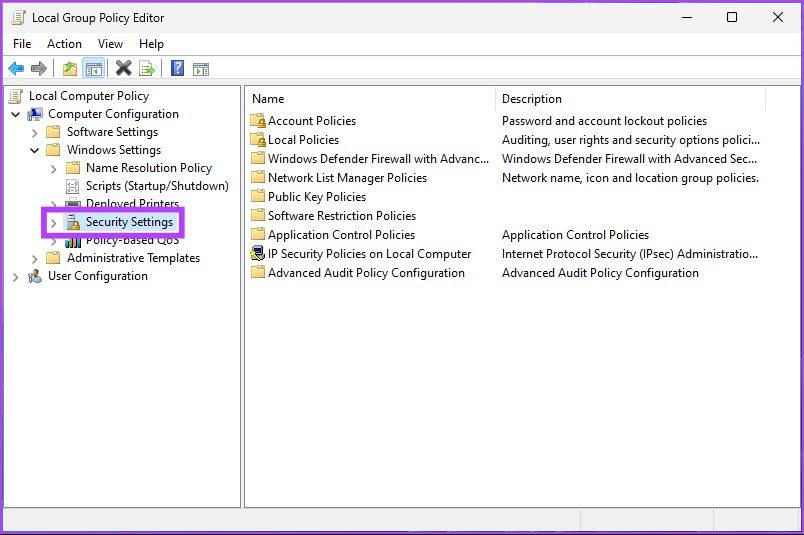
Step 4: Select the Security Settings option.
Take Control Over Your Windows Security
Whether you are a system administrator or just a user looking to secure your device, knowing how to open Local Security Policy in Windows can save you time and ensure that it is available when you need it. You may also want to read how to fix Windows Security Center is turned off error. The above article may contain affiliate links which help support Guiding Tech. However, it does not affect our editorial integrity. The content remains unbiased and authentic.